Customize Function
Add customize formula functions
To add customize function, use the FormulaExtension class. The following example that adds a function to make given string uppercase.
unvell.ReoGrid.Formula.FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions["myUpper"] =
(cell, args) =>
{
if (args.Length == 0)
{
// this function needs at least one argument
return null;
}
return Convert.ToString(args[0]).ToUpper();
};
Test this function, input the formula =myUpper("hello"): 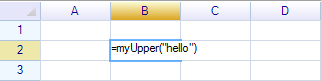
Press enter, the cell value will be changed to uppercase. 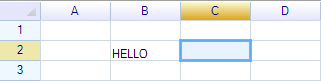
About FormulaExtension
The FormulaExtension is an interface to add extensions during formula calculation.
In the ReoGrid Extension version with scription execution feature, the formula extension can be implementated by some ReoScript features. For applications use ReoGrid standard version, the FormulaExtension interface is more simple way to make formula extension features.
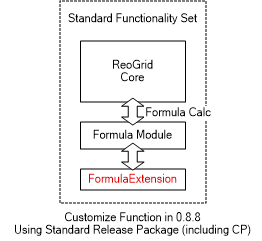
The CustomFunctions property is defined as:
Dictionary<string, Func<ReoGridCell, object[], object>> CustomFunctions
Simplest function example
C#:
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions["myFunc"] = (cell, args) => {
// function body goes here
return null;
};
VB.NET:
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions("myFunc") = Function(cell, args)
' function body goes here
Return Nothing
End Function
Using delegate function
It's also possible to use normal delegate function rather than lambda expression. To define a function:
C#
static object MyFunc(ReoGridCell cell, params object[] arguments)
{
return null;
}
To make this static method available in formula as customize function:
VB.NET
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions["myFunc"] = MyFunc;
Shared Function MyFunc(cell As ReoGridCell, ParamArray args As Object()) As Object
Return Nothing
End Function
To make this shared method available in formula as customize function:
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions("myFunc") = AddressOf MyFunc
Cell instance
The first argument is the cell instance that is the owner of the formula, this function now is called from the formula, for example:
worksheet["A1"] = "=myFunc()";
The A1 cell has a formula that calls the customize function "myFunc", the function body in .NET code defined above will be invoked, the cell argument is the "A1" cell.
static object MyFunc(ReoGridCell cell, params object[] arguments)
{
MessageBox.Show(cell.Position.ToAddress()); // output: A1
return null;
}
Get worksheet instance from function
By getting the property Worksheet of cell instance to get worksheet instance, as well as the workbook instance from Workbook property of worksheet instance.
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions["myFunc"] = (cell, args) =>
{
var worksheet = cell.Worksheet;
var workbook = worksheet.Workbook;
...
return null;
};
Limit the function scope only available in specified workbook or worksheet:
{
var worksheet = cell.Worksheet;
var workbook = worksheet.Workbook;
if (workbook != myWorkbook)
{
// not in valid workbook scope
return null;
}
}
Get function arguments
The second argument is the arguments passed from caller in formula.
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions["myFunc"] = (cell, args) =>
{
if (args.Length < 2)
{
// this function requires at least two arguments
return null;
}
return null;
};
Data type in formula
There are various types of data used during formula calculation:
- Number (int, long, short, float, double)
- String (string and StringBuffer)
- Boolean
- DateTime
- Object
ReoGrid always use double as the number type in formula calculation. ReoGrid performs the following conversions before value passed into functions:
- int, long, short, float will be converted into double
- string and StringBuffer object will be converted into string
Numeric constants
Numeric constants used in formula will be initialized as double type, for example:
worksheet["A1"] = "=myFunc(10)";
The number 10 will be parsed and stored in memory as double type. The first argument in argument array will be double type.
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions["myFunc"] = (cell, args) =>
{
if (args.Length < 1 || !(args[0] is double))
{
// this function requires a double value
return null;
}
...
};
Numeric variables
When the numeric value was given from a cell, it will be converted into double type. Create the following function:
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions["myFunc"] = (cell, args) =>
{
double value = (double)args[0];
return value \* 2;
};
Then use it in formula:
sheet["A1"] = (int)10;
sheet["B1"] = "=myFunc(A1)";
There will no data type conversion error happen. (But be careful the argument length)
References in function
Cell reference
ReoGrid will get the value from referenced cell that is used in formula automatically, like the example of 'Numeric variables'.
Range reference
If a range literal used in formula, ReoGrid will pass RangePosition struct into function, for example:
worksheet["G2:K3"] = new object[] { 1, 2, 5, 7, 8, 10, 12, 15, 16, 19};
worksheet["L2"] = "=CountEvenNumber(G2:K3)";
There is a range reference (G2:K3) that was used in the formula, it's necessary to handle it manually inside customize function body. Following example function that counts the even numbers from given range:
FormulaExtension.CustomFunctions["CountEvenNumber"] = (cell, args) =>
{
if (args.Length < 1 || !(args[0] is RangePosition))
{
return null; // we need a range reference
}
RangePosition range = (RangePosition)args[0];
int count = 0;
// iterate over cells inside a range
cell.Worksheet.IterateCells(range, (r, c, inCell) => {
double value;
// try get a number from cell data
if (ReoGridCellUtility.TryGetNumberData(inCell.Data, out value) {
if ((value % 2) == 0) {
count++;
}
}
// continue iterate
return true;
});
return count;
};
Name reference
Name to cell
If a name reference to a cell, the cell's value will be get and passed into the function automatically.
worksheet.DefineNamedRange("r1", "A1");
sheet["r1"] = (int)20;
sheet["B1"] = "=myFunc(r1)";
Name to range
If a name reference to a range used in formula, ReoGrid will find the range by the name firstly, then pass the RangePosition struct object, it could be handled like range reference.
worksheet.DefineNamedRange("evenRange", "G2:K3");
worksheet["evenRange"] = new object[] { 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15, 17 };
worksheet["I2"] = "=CountEvenNumber(evenRange)";
AssertSame(worksheet["I2"], 4);
Customize name reference provider
It's possible to add constant value that is used in formula but provided by .NET program. The following example adds two names that return different two constant values:
unvell.ReoGrid.Formula.FormulaExtension.NameReferenceProvider =
(cell, name) =>
{
if (name == "myName1")
return 10;
else if (name == "myName2")
return 20;
else
return null;
};
The NameReferenceProvider is defined as:
Func<ReoGridCell, string, object> NameReferenceProvider { get; set; }
Test the name 1, input =myName1 in cell: 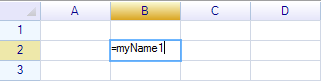
The name returns value 10: 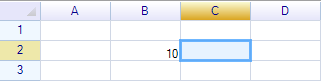
Input =myName2 in cell: 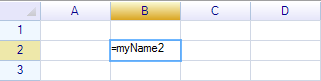
The name returns value 20: 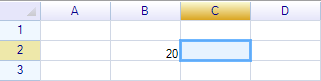
Add mathematical constants
By using the customize name reference provider, it's also possible to add some constants such as mathematical numbers, the following code defines a constant provider:
VB.NET:
Shared Function MathConstantProvider(cell As ReoGridCell, name As String) As Object
Select Case (name)
Case "PI"
Return Math.PI
Case "E"
Return Math.E
Case "MyConst"
Return 1.23456
End Select
Return Nothing
End Function
Apply this name reference provider:
FormulaExtension.NameReferenceProvider = AddressOf MathConstantProvider
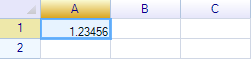
And use the constant in formula:
worksheet("A1") = "=MyConst"
Result:
Combine customize function and customize name provider
Using customize name provider in a customize function is also supported. The name will be converted into value and passed into functions.
FormulaExtension.NameReferenceProvider = (cell, name) =>
{
switch (name)
{
case "Pi": return Math.PI;
case "E": return Math.E;
default: return null;
}
};
Use the name Pi in customize function:
worksheet["D3"] = "=Div100(Pi)";
AssertSame(worksheet["D3"], Math.PI / 100);
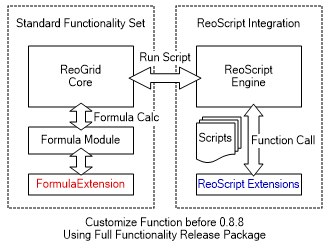
Add ReoScript language customize function
When the ReoScript module extension is enable, ReoScript script language could be used to handle the cell's data, style, border, data formats and etc, it's similar to the VBA in Excel. ReoScript supports that make .NET extension for script language, including call .NET functions in script.
ReoGrid supports that invoke ReoScript customize extension functions:
ReoScript language extension is only available in Full release package.
Add ReoScript function in C#
Add customize function to extend control:
workbook.Srm["sqrt"] = new NativeFunctionObject("sqrt", (ctx, owner, args) =>
{
if (args.Length < 1)
return NaNValue.Value;
else
return Math.Sqrt(ScriptRunningMachine.GetDoubleValue(args[0], 0));
});
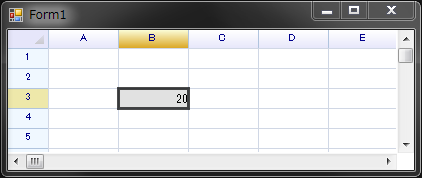
Test:
var worksheet = workbook.CurrentWorksheet;
worksheet[2, 1] = "=sqrt(400)";
Double click on cell to view its formula: 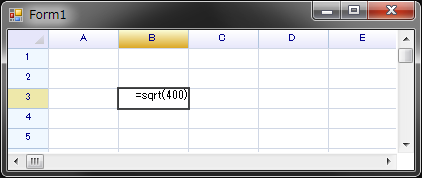
Customize function can also be used in script.
Customize functions in ReoScript context
Object 'workbook' is the global object which is available in both formula and script. (same as 'window' in JavaScript) 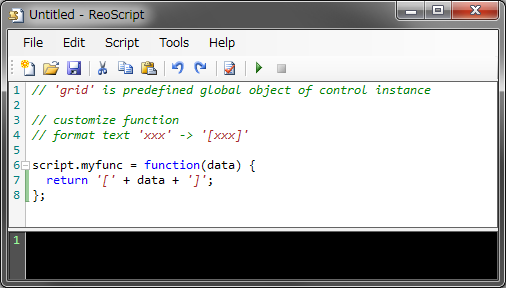
Run the code above once and use it in formula. 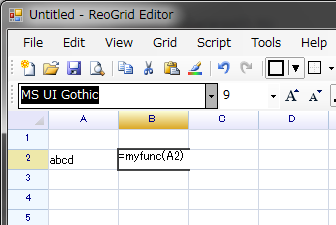
Press 'enter': 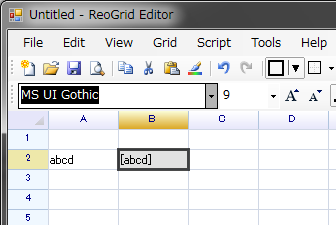
Run Script to add functions in C#
It is also possible to run the script to create ReoScript functions in C#, below is the ReoScript lambda expression used to create new function.
grid.RunScript("script.myfunc = data => '[' + data + ']';");